The Birth of Soft Torture
CIA interrogation techniques—a history.
By Rebecca LemovUpdated Wednesday, Nov. 16, 2005, at 5:07 PM ET
In 1949, Cardinal Jószef Mindszenty appeared before the world's cameras to mumble his confession to treasonous crimes against the Hungarian church and state. For resisting communism, the World War II hero had been subjected for 39 days to sleep deprivation and humiliation, alternating with long hours of interrogation, by Russian-trained Hungarian police. His staged confession riveted the Central Intelligence Agency, which theorized in a security memorandum that Soviet-trained experts were controlling Mindszenty by "some unknown force." If the Communists had interrogation weapons that were evidently more subtle and effective than brute physical torture, the CIA decided, then it needed such weapons, too.
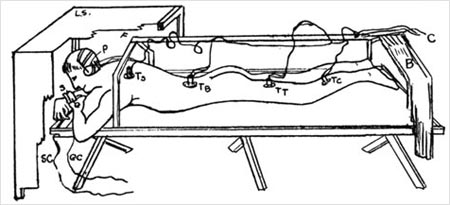 |
| Illustration of an experiment run by Hull at Yale on university students in 1937. |
Months later, the agency began a program to explore "avenues to the control of human behavior," as John Marks discusses in his book The Search for the Manchurian Candidate. During the next decade and a half, CIA experts honed the use of "chemical and biological materials capable of producing human behavioral and physiological changes" according to a retrospective CIA catalog written in 1963. And thus soft torture in the United States was born...
The rest of the article is available at www.slate.com/id/2130301?nav=nw





No comments:
Post a Comment